Under AGP-free: Effective measures to remove anti-nutritional factors in soybean protein
- Christy

- Sep 10, 2020
- 4 min read
Updated: Mar 17, 2021
Under AGP-free, the key to nutrition design of feed is to ensure the intestinal health, reduce diarrhea, and promote growth. There are two core ways to ensure intestinal health, that is to protect the structure and prevent damage to the intestinal cells, and to keep balance of the intestinal bacteria flora. For intestinal cell structure, one of the reasons for the destruction is the toxic and harmful substances brought by feed. The main protein sources in feed, such as soybean protein, contains many types and high contents of anti-nutritional factors. When exceeding a certain ratio, it will destroy the intestinal cell structure and break the balance of bacteria flora, thus reduce the digestion and absorption capacity of animals, increase diarrhea, and inhibit growth. Therefore, removing the anti-nutritional factors in soy protein is one of the effective measures to reduce animal intestinal damage and maintain intestinal health

Types, physical and chemical indexes and mechanisms of anti-nutritional factors in soy proteins
Soy proteins are widely used in animal feed. But soybeans actually contain varieties of anti-nutritional factors, which restrain the dosage of soy proteins in animal feed. Let's take a look at the type, content, physical and chemical indexes and anti-nutritional mechanism of anti-nutritional factors in soybeans. After understanding these anti-nutritional factors, we can take corresponding measures to eliminate or reduce them.



Effective measures to clear anti-nutritional factors
According to the physical and chemical properties of the main anti-nutritional factors in soybeans, thus physical (high temperature, high pressure), chemical (alcohol, acid), and biological (fermentation, enzymolysis) processes can be used to remove or degrade the anti-nutritional factors.
(1). Antigens
The antigens are mainly glycinin and β-conglycinin with a special spatial structure. By destroying the allergenic subunits in the quaternary and tertiary structure of the antigen protein, can reduce the anti-nutritional effects.
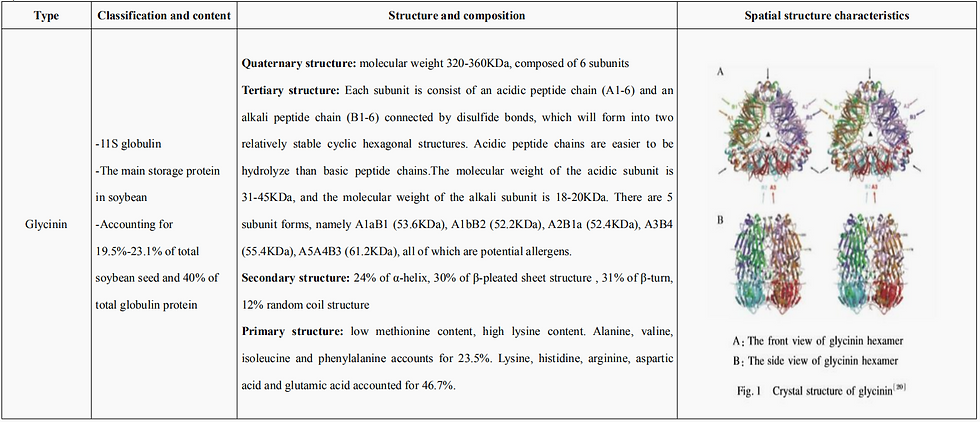

High pressure and high temperature can change the quaternary and tertiary structure of the antigen protein, enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation process can destroy the quaternary and tertiary structure of the protein, and even degrade the secondary and primary structure.
When extruded soybeans and soybean protein concentrate are treated with high temperature and high pressure, and the antigen protein clearance rate could reaches to 50-70%; the fermented soybean meal antigen protein clearance rate could be different under different strains and fermentation conditions, and the average rate is 50%; for combined enzymatic hydrolysis process, enzymes will be selected and reaction condition will be controlled based on protein structure characteristics, the clearance rate could be more than 90%.

(2) Trypsin inhibitors
There are about 7-10 trypsin inhibitors, but currently only two trypsin inhibitors have been studied extensively, namely Kunitz type trypsin inhibitor (KTI) and Bowman. Birk type trypsin inhibitor (BBI). They all have an active center that binds to protease, inhibiting protease activity. Thus, destroying the active center can reduce the anti-nutritional effect.

High temperature can destroy the conformation of the active center of trypsin inhibitor. Enzymolysis and fermentation can change the spatial structure of trypsin inhibitor, and even degrade the secondary and primary structure, thereby destroying its active center. The high temperature clearance rate is 75-95%, and the clearance rate of fermentation is 50-90% with different strains and react conditions; the combined enzymatic hydrolysis clearance rate could reach to 90%.

(3) Oligosaccharides
Soybean oligose (or oligosaccharides): the saccharides formed by 2-10 monosaccharide molecules connected by glycosidic bonds. It is the general term for soluble saccharides in soybeans, mainly including sucrose (disaccharide), raffinose (trisaccharide) and stachyose ( tetrasccharide).
α-galactosides: refers to oligosaccharides composed of one or two galactoses connected with α-1, 6 glycosidic bonds (such as raffinose , which is a irreducible trisaccharide formed by galactose, glucose and fructose; Sucreose, which is a irreducible tetrasccharide composed of lactose, galactose, glucose, fructose; verbascose, etc.), due to the lack of enzymes that decompose α-galactosides in the small intestine of animals, they can only enter the large intestine and be used by microorganisms.
The anti-nutritional effect of soybean oligosaccharides will be affected by the dosage.When the content in the feed is low, it is used by bifidobacteria to produce short-chain fatty acids, reduce pH, inhibit harmful bacteria, and help improve the structure of animal intestinal bacteria flora and improve the production performance of animals. But when the content is too high, it will be fermented by harmful bacteria to produce carbon dioxide, hydrogen and a small amount of methane gas, causing abdominal distension, bowel irritation, diarrhea, etc., resulting in reduced animal performance.
Studies have found that 1% of stachyose in nursery feed is beneficial to growth, and 2% and above reduce growth performance (Zhang, 2003; Pan Haibao, 2011); raffinose in nursery feed at 0.4% is beneficial to growth, and 0.8% and above reduce growth performance (Liu Ling, 2017). Therefore, the dosage of oligosaccharides need to be controlled in feed as conditioned anti-nutritional factors. The most effective way to remove oligosaccharides is the enzymatic hydrolysis process. By using α-galactosidase to hydrolyze stachyose and raffinose, the clearance rate can reach to 70-80% (Shang, 2018; Pan Baohai, 2011)

【Summary】
The main components of anti-nutritional factors in soy protein are antigen proteins, trypsin inhibitors, and oligosaccharides, which need to be deep processed to reduce in order to improve their application value in feed.
In actual production, high temperature, high pressure, fermentation, and enzymatic hydrolysis can eliminate antigen proteins and trypsin inhibitors in a certain extent, and enzymatic hydrolysis can specifically eliminate oligosaccharides.
Enzymatic hydrolysis can remove more than 90% of the anti-nutritional factors in soybeans and effectively reduce the intestinal damage to the animals. Therefore, the soy protein processed by enzymatic hydrolysis is one of the best choices for AGP-free feed and protecting of intestinal health of animals!
Annex. Content of ANF in each protein raw material









Comments