Analysis of Raw Materials: Health-care Value of Protein Raw Materials through Different Processes
- Christy

- Jan 11, 2024
- 2 min read
Ⅰ Background
Fish meal and other high-quality protein raw materials continue to be in tight supply and high prices. Feed companies have been looking for new high-quality functional protein to control costs and quality. High-quality functional proteins should have the characteristics of “two high and two low”, including high nutritional value, high health-care value, low content of ANF and low bio-safety risks.
The health-care value of protein arise from the functional components presenting in the raw material, as well as from deep processing of raw materials, primarily small peptides. These components enhance the digestion, absorption, and deposition capacity of animals. There is an increasing number of protein ingredients from various sources and processes that have emerged. How can feed companies efficiently assess the functional components of raw materials? We will demonstrate how to assess the health-care value and current quality status of proteins mainly about small peptides in this section. We hope to provide a reference for effectively selecting protein raw materials.
Ⅱ Content
1.Evaluation methods
2.Test results
(1) Content of acid soluble protein
【Test results】
【Analysis】
When excluding free amino acids and other nitrogenous substances from the raw materials, a higher acid-soluble protein content corresponds to a higher peptide content.
The raw materials are processed extensively to break down large molecule proteins into medium-long chain peptides, small peptides, and amino acids. Extruding and concentrate methods can not degrade the protein structure, while fermentation can degrade the protein into medium-long chain peptides, containing 5-15% of acid-soluble protein. Enzymatic treatment can degrade the protein to medium-long chain peptide, small peptides, containing 30% or more acid soluble protein. Yeast hydrolysate can be degraded into small peptides, free amino acids, containing 30-40% of acid soluble protein.
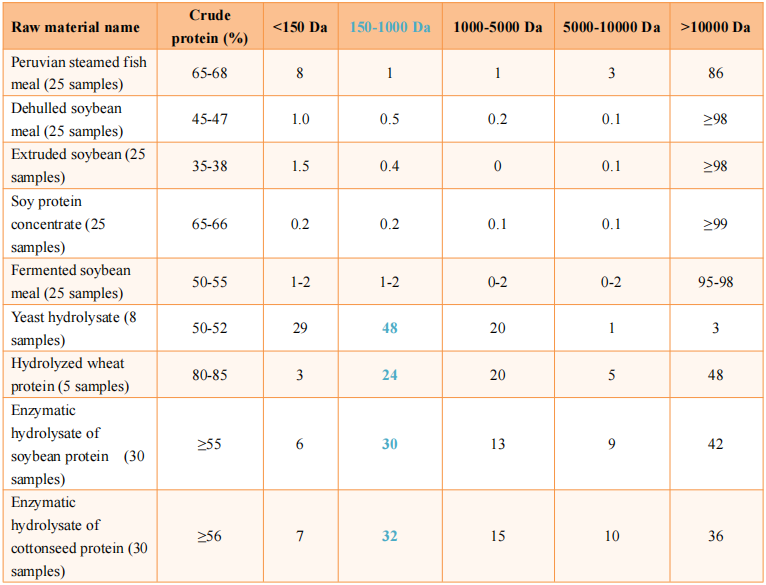
(2) Content of small peptide
【Test results】
【Analysis】
The higher the percentage of the protein molecular weight range of 150-1000Da, the greater the content of 2-6 peptides.
Protein ingredients undergo extensive processing to break down large molecular proteins into peptides of varying molecular weights. Extruding, concentration, and fermentation treatments do not degrade large molecular proteins to small peptides, while enzymatic process can break it into peptides range of 150-1000 Da, up to 20% or more.
(3) Structure of small peptide
【Test results】
【Analysis】
National Food Research Center of Jiangnan University found that enzymatic functional protein produced by Chengdu Mytech contain Glu-Tyr and Ala-Phe through the identification, isolation and purification of bio-active peptides. The content of these peptides reaches milligram level, which is a very high content in food and health-care products.
(4) Antioxidant capacity
【Test results】
【Analysis】
The in vitro antioxidant capacity of raw materials is correlated with the animals’ in vivo antioxidant capacity.The higher the ABTS value, the stronger the antioxidant capacity.
Protein raw materials ABTS antioxidant capacity value are positively correlated with 150-1000Da values. The small peptides in hydrolysate yeast, enzymatic hydrolysate of soybean protein, and enzymatic hydrolysate of cottonseed protein range of 150-1000Da account for 30%, while the ABTS value reaches 30 mmol/kg. It shows that the higher the degree of enzymatic degradation of raw materials, the higher the content of small peptides and the stronger the antioxidant capacity.












Comments